In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping how businesses approach content creation. This profound shift has naturally given rise to a pressing question for small business owners: “Can Google detect AI content created by a free AI writer?” Many small businesses, often constrained by limited time, budget, or specialized expertise, view AI writers as a compelling solution to consistently populate their websites and blogs with engaging content.
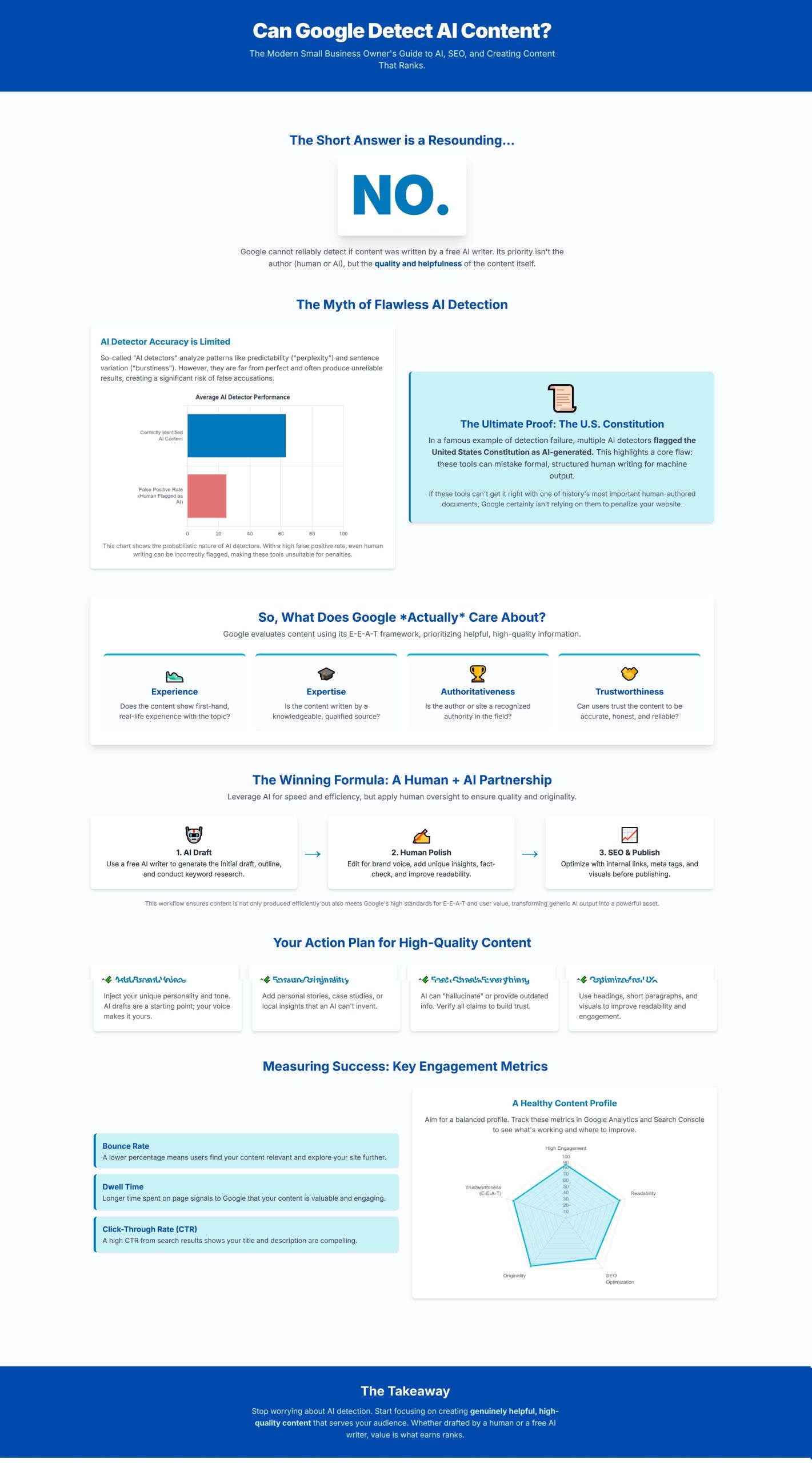
The direct answer to this central question is straightforward: Google cannot reliably detect AI-generated content.
A striking illustration of this unreliability occurred when the United States Constitution, a foundational human-authored document, was mistakenly flagged as AI-generated by multiple detection tools. This incident powerfully underscores the inherent limitations and flaws in current AI detection technologies. What truly holds significance for Google is not the origin of the content, but rather its ability to effectively address a user’s query with clarity, depth, and relevance, prioritizing what Google terms “helpful content” above all else.
This report will delve deeply into Google’s evolving stance on AI, explore the technical limitations that render AI detection unreliable, highlight the paramount importance of Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) framework, and provide practical strategies for small businesses to safely and effectively use AI writers. The aim is to offer actionable steps that ensure content produced with a “free AI writer” not only meets Google’s stringent quality standards but also genuinely serves the target audience, ultimately leading to improved search rankings and sustainable business growth.
Google’s Evolving Stance on AI-Generated Content: Clarity amidst Confusion
Google’s official position on AI-generated content has undergone a notable transformation over recent years. Historically, the search giant expressed caution, often associating “auto-generated content” with spammy practices primarily designed to manipulate search rankings rather than provide genuine value to users. This early stance suggested a focus on the method or origin of content creation.
However, a pivotal shift in Google’s guidelines became evident in 2023 and 2024. The updated directives clarified that the emphasis is no longer on who authored the content, but fundamentally on how useful that content is to the reader. As articulated by Google Search Central, “Using automation—including AI—to generate content with the primary purpose of manipulating ranking in search results is a violation… However, not all use of automation is spam“. This means that if a “free AI writer” is employed to create content that delivers authentic value, comprehensively answers user questions, and demonstrates expertise, it operates within Google’s established guidelines.
This evolution in Google’s approach represents a significant paradigm shift. The focus has moved from evaluating content based on its source to assessing its inherent quality and its ability to satisfy user intent. This change implies that AI is increasingly viewed as merely another tool in a content creator’s arsenal, much like a word processor or a research assistant. The critical factor now resides in how that tool is utilized to produce the final output. This reorientation empowers small businesses, as it removes an inherent penalty simply for using AI, provided their content prioritizes quality and user value.
Understanding Google’s Helpful Content System and Its Implications for AI
The core mechanism through which Google manages content quality, particularly in the context of AI, is its “Helpful Content System.” Updates to this system, notably those rolled out in March 2024 and January 2025, were specifically designed to reduce the presence of unoriginal and unhelpful content in search results by approximately 40%.
These updates provide explicit instructions to Google’s quality raters. They are directed to assess if the main content of a page is “auto or AI generated, and if so, rate it low” only if it is glaringly obvious, generic, or lacks originality. Content generated rapidly or at scale using AI, “without much editing, research, or added insight,” is flagged as problematic. Similarly, pages that merely summarize, copy, or rephrase existing material without contributing original value are also penalized.
The crucial understanding here is that Google is not imposing an outright ban on AI content. Instead, it is refining its ability to identify and de-prioritize “low-effort” content—material that feels mass-produced, repetitive, or appears to be written primarily for search engine manipulation rather than to genuinely assist users. This indicates that Google’s strategy to combat low-quality, scaled AI content is not through a direct “AI detector.” Rather, it’s through its sophisticated helpful content algorithms that evaluate broader quality signals, such as a lack of originality, minimal effort, and repetitiveness, which often correlate with AI used without human oversight. Consequently, small businesses should concentrate their efforts on human editing and adding unique value, rather than attempting to circumvent a non-existent AI detection system.
The Truth about AI Content Detection: Why It’s Unreliable
The question of whether Google can detect AI content created by a free AI writer often leads to a discussion of AI detection tools. Tools like Originality.ai, ZeroGPT, and Copyleaks purport to identify AI-generated text by analyzing specific writing patterns. These tools frequently rely on metrics such as “perplexity” and “burstiness” to make their assessments. Perplexity measures the predictability of a word sequence; AI-generated text typically exhibits lower perplexity due to its adherence to common linguistic patterns, whereas human writing often includes more unexpected word choices, leading to higher perplexity. Burstiness, on the other hand, refers to variations in sentence length and structure. Human writing naturally incorporates a dynamic rhythm with a mix of short and long sentences, while AI-generated text can often appear “too perfect” or uniformly structured.
The Inherent Flaws and Limitations of AI Detectors: Acknowledging Imperfection
Despite the claims of these detection tools, their accuracy is far from foolproof, and they frequently struggle to reliably distinguish between human and machine-generated content. A significant challenge lies in their propensity for false positives and false negatives. A false positive occurs when human-written content is erroneously flagged as AI-generated, while a false negative happens when AI-generated text goes undetected. Studies have indicated that commercially available AI detectors correctly identify AI content only about 63% of the time, with false positive rates reaching as high as 25%.
Furthermore, these detectors can exhibit bias, struggling with specific writing styles. They may unfairly flag content by creative writers, students, or non-native English speakers as AI-generated simply because their linguistic patterns deviate from the training data the tools were exposed to. As AI models become increasingly sophisticated and capable of producing more human-like text, detection becomes even more challenging. Advanced AI models generate text with greater variability, making it difficult for detectors to keep pace with their evolution. The effectiveness of these tools is further diminished when AI-generated text undergoes human revision, as this process significantly complicates its identification as AI-produced. Even paraphrasing AI-generated text through a second large language model can defeat watermarking attempts. Ultimately, AI detection tools offer probabilistic results rather than definitive proof. A high AI-likelihood score is merely an estimation, not a conclusive judgment; they are, at best, “educated guesses”.
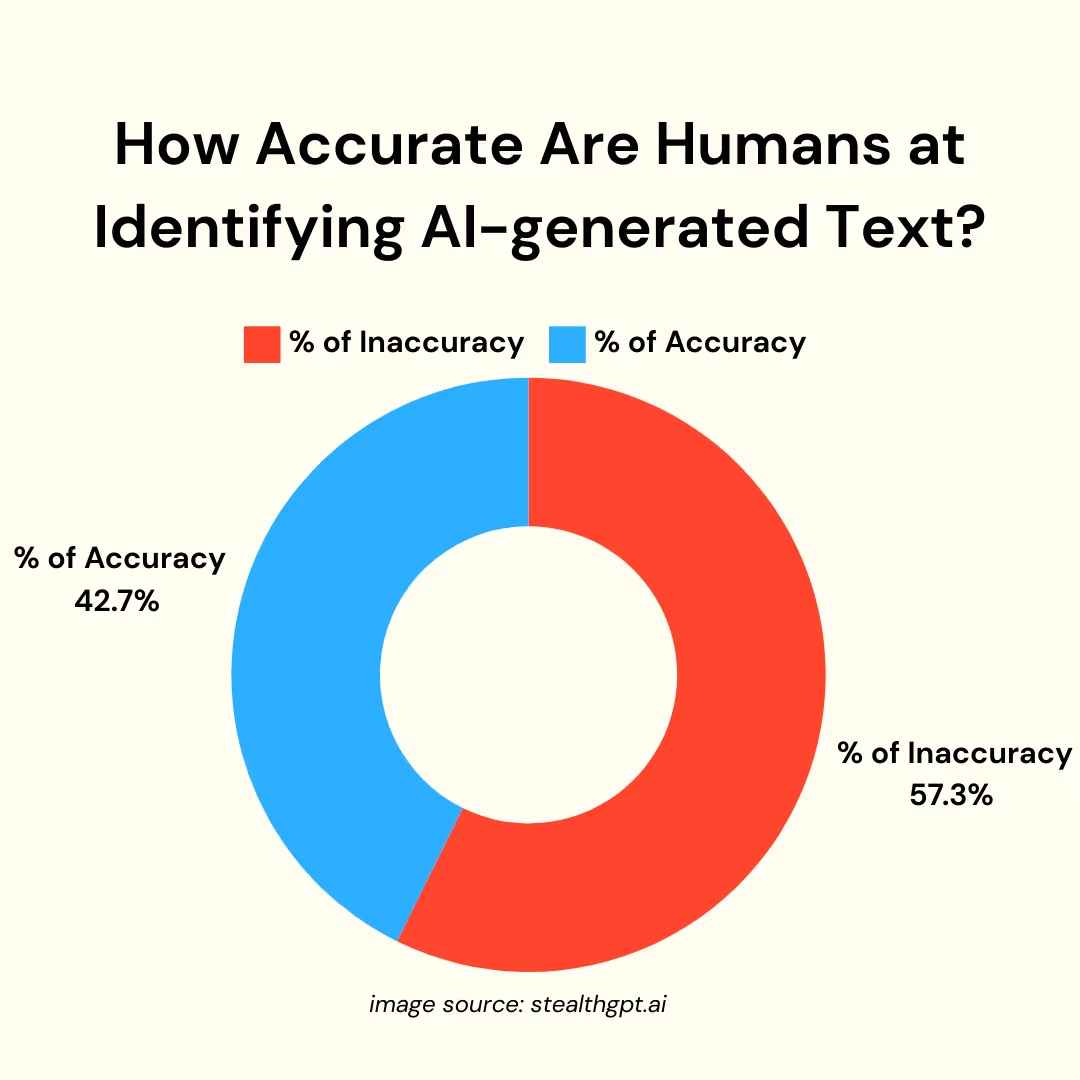
The fundamental design of AI detectors, which relies on pattern recognition, inherently leads to these false positives, particularly when confronted with sophisticated human writing or advanced AI models. Detectors analyze predictability and sentence variation, and while human writing, especially formal or academic prose, can naturally exhibit predictable patterns and consistent sentence structures, it can inadvertently mimic the “signature” of AI writing. Conversely, advanced AI models are engineered to emulate human variability, making them increasingly difficult for detectors to identify. This creates a perpetual cat-and-mouse game where detection tools are constantly lagging behind AI advancements, leading to their inherent unreliability for definitive judgments in critical applications like academic integrity or search engine penalties.
The Infamous US Constitution Example and Other Instances of Detection Failures
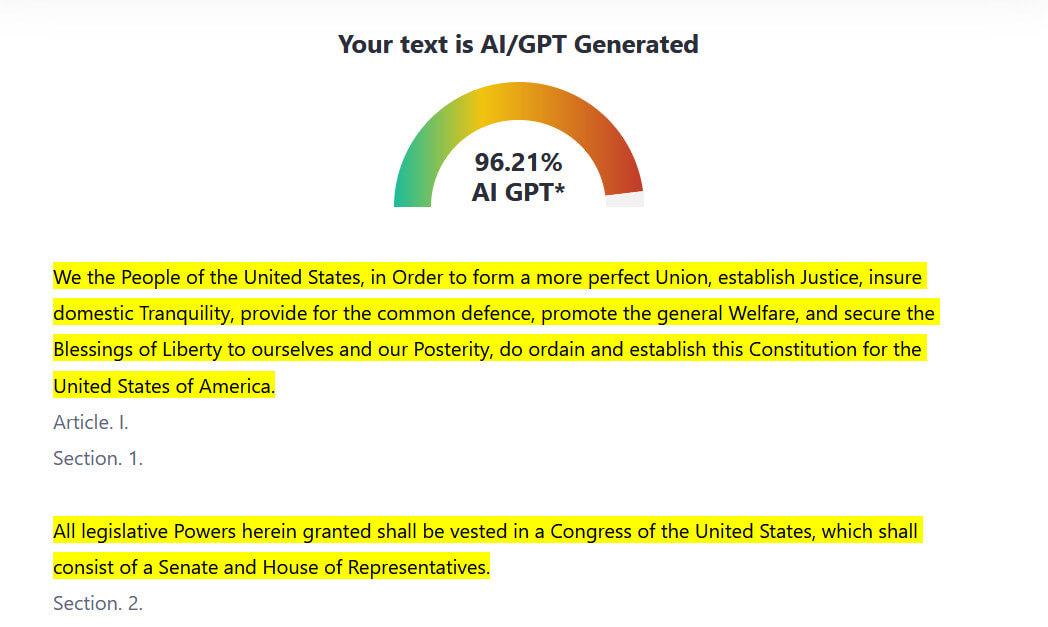
The most widely cited and compelling example of AI detection failure involves the United States Constitution. This foundational document, penned centuries before the advent of artificial intelligence, was astonishingly flagged as AI-generated by multiple prominent detection tools, including GPTZero and Copyleaks. This incident raises a crucial question: How could such a historically significant, human-authored text be mistaken for machine output? The explanation lies in the fact that these tools rely on identifying linguistic patterns that can, at times, overlap with the characteristics of high-level, formal human writing.
Beyond the Constitution, similar misidentifications have occurred with other venerable texts. For instance, sections from the Bible have also been erroneously flagged as AI-generated. These examples serve as powerful demonstrations of the unreliability and profound limitations inherent in current AI detection technology.
Why Google Doesn’t Rely on These Tools for Penalties: A Strategic Choice
Given the significant unreliability and high rates of false positives demonstrated by AI detection tools, it becomes clear that Google “certainly isn’t basing penalties on it”. Google’s primary objective is to deliver “the most useful information” and “helpful content” to its users. If Google were to rely on these flawed tools for penalization, it would inevitably result in the unjust demotion of a substantial amount of high-quality, genuinely helpful human-written content. Such an outcome would directly contradict its core mission and severely degrade the quality of its search results for users.
Instead, Google’s algorithms are designed to focus on more robust and user-centric signals. The search engine explicitly states that it utilizes “user engagement metrics, content depth, bounce rate, and authority as ranking factors”. This strategic choice allows Google to avoid the risk of harming its own search quality and user trust by not relying on fallible AI detectors. This approach reinforces that Google’s algorithms are sufficiently sophisticated to evaluate content based on its inherent value and how users interact with it, irrespective of the method used for its creation.
The decision by Google not to rely on these unreliable tools for penalties is a strategic one, aimed at preventing the penalization of legitimate content and maintaining a focus on user experience. Since AI detectors frequently misclassify human-written content as AI, relying on them would lead to the unjust demotion of valuable, genuinely helpful content, directly undermining Google’s mission. By prioritizing user engagement and content quality signals, Google ensures its algorithms assess content based on its intrinsic value and user interaction, rather than its origin.
Table: Limitations of AI Content Detection Tools
|
Beyond Detection: The E-E-A-T Framework for Content Quality
Google’s core ranking algorithm is fundamentally driven by the concept of E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. This framework, introduced in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines, is how Google evaluates the quality and credibility of content. It is not merely an SEO acronym but a comprehensive set of principles that guide Google in determining which content is most helpful and reliable for its users.

- Experience (E): This element considers whether the content creator possesses genuine first-hand or life experience relevant to the topic discussed. For instance, a travel blogger narrating personal journeys or a DIY guide featuring step-by-step visuals demonstrates direct engagement and practical application.
- Expertise (E): This assesses whether the content is produced by someone with proven knowledge or qualifications in the subject matter. It involves citing credible sources, referencing industry experts, and backing claims with data-backed studies.
- Authoritativeness (A): This refers to whether the content creator or website is recognized as a go-to, reliable source within their community or niche. This can be demonstrated through positive reviews, backlinks from reputable sites, mentions in the media, and a strong online reputation.
- Trustworthiness (T): This is arguably the most crucial element, evaluating if users can depend on the content to be accurate, honest, safe, and reliable. It includes citing credible sources, providing honest information, having a secure website (HTTPS), and transparent contact details.
Demonstrating E-E-A-T directly influences Google’s perception of content quality, which in turn significantly impacts search rankings and user engagement. Google’s algorithms utilize signals that align with E-E-A-T, such as authoritative backlinks, content relevance, and user engagement, to determine content quality. While E-E-A-T itself is not a direct ranking factor, the feedback from human quality raters, who assess content based on these guidelines, helps refine Google’s algorithms to prioritize E-E-A-T-aligned content in the future. This creates a continuous feedback loop where content exhibiting these qualities is favored.
For small businesses, E-E-A-T transcends being merely an SEO tactic; it is a foundational business practice that cultivates trust with both Google and, more importantly, with customers. Local customers, in particular, seek businesses they can trust. Elements such as authentic customer reviews, consistent Name, Address, and Phone Number (NAP) information, and transparent author bios directly contribute to building this trust. Ultimately, trust is paramount for converting website visitors into loyal customers. This means that focusing on E-E-A-T not only enhances search engine visibility but also directly contributes to real-world business success and customer loyalty.
Even content created with a “free AI writer” can effectively tick these E-E-A-T boxes, especially when it is informative, directly answers search queries, is well-structured with clear headings and bullet points, and is meticulously edited by humans for clarity and nuance. Small businesses can absolutely leverage AI to publish helpful, SEO-rich content, provided they consistently prioritize the user’s needs.
Table: E-E-A-T Checklist for Small Businesses: Demonstrating Credibility
| E-E-A-T Element | How to Demonstrate (Especially with AI-Assisted Content) |
| Experience |
Share Real-Life Examples & Case Studies: Incorporate personal anecdotes, detailed case studies, and first-hand insights. Use visuals (photos, videos) or tutorials to show direct engagement. Include User Reviews with Photos: Authenticity builds trust. |
| Expertise |
Showcase Author Credentials: Use detailed author bios with qualifications, professional background, and links to portfolios. Cite Trusted Sources & Experts: Back claims with research, data, and quotes from industry experts or accredited institutions. Publish Expert-Level Content: Go beyond sales talk; create blog posts, FAQs, and service pages that offer unique insights and actionable advice. |
| Authoritativeness |
Build Quality Backlinks: Actively seek backlinks from reputable sites, local directories, and industry leaders. Mention Press Coverage/Awards: Highlight any media mentions, awards, or community involvement. Consistent NAP & Google Business Profile: Ensure business information is accurate and consistent across all platforms. |
| Trustworthiness |
Accurate & Fact-Checked Content: Ensure all information is well-researched, accurate, and properly cited. Website Security (HTTPS): A secure site indicates professionalism. Clear Contact Information & Policies: Make contact details, privacy policies, and terms of service easily accessible. Display Testimonials & Reviews: Showcase positive customer feedback and industry awards prominently. Regular Content Updates: Keep content fresh and accurate by regularly updating old articles with new insights and information. |
Strategic AI Content Creation: The Human-AI Partnership
The most effective approach to using a “free AI writer” for content creation involves a strategic partnership: leveraging AI to draft, and humans to polish. This workflow ensures that while AI handles the heavy lifting of generating initial content, human oversight injects the necessary quality, nuance, and originality that Google and users demand.
The “AI to Draft, Human to Polish” Workflow
The recommended process for small business owners is to use the AI tool to generate a strong first draft. This initial output can then be refined by a human editor. This human touch is critical for several reasons: it removes fluff, clarifies complex points, and adds original examples or local insights that AI cannot spontaneously generate.
Human editing serves as the critical bridge that transforms raw AI output into high-quality, E-E-A-T compliant content, effectively mitigating AI’s inherent limitations. AI-generated content, left unedited, can often feel generic, robotic, or lack the subtle nuances that resonate with human readers. It may also fail to capture a brand’s unique voice or inject the specific, first-hand experience that demonstrates true E-E-A-T. The necessity of human review to add originality, brand voice, contextual relevance, and to ensure factual accuracy creates a direct link: AI drafts the foundation, but human intervention transforms it into content that is not only rankable but also trustworthy and engaging for the audience.
Best Practices for Human Editing AI Output
To ensure AI-generated content meets high standards, human editors should focus on:
- Adding Nuance and Brand Voice: AI tools, while proficient at mimicking patterns, often lack the personal touch and emotional depth that define a unique brand voice. Editors must infuse the brand’s personality, tone, and specific phrasing. This involves training the AI with brand voice guidelines and examples, then meticulously reviewing outputs to ensure consistency across all channels. A “We’re This, Not That” list can be invaluable for guiding AI and human editors alike.
- Ensuring Originality and Unique Insights: AI algorithms are trained on existing data, which can lead to derivative or repetitive content if not carefully managed. Human editors must add original thoughts, real-life examples, local insights, and specific stories or testimonials that only a human connected to the business could provide. This transforms generic information into truly helpful and unique content.
- Fact-Checking and Accuracy: AI can sometimes “hallucinate” or provide inaccurate information, especially when asked for sources. Rigorous fact-checking is paramount to ensure the content is reliable and precise, particularly for “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) topics that impact a person’s health, finances, or well-being.
- Improving Legibility and Flow: While AI can produce grammatically correct text, it might lack the natural flow and readability of human writing. Editors should refine sentence structure, break up long paragraphs, and use headings, bullet points, and clear takeaways to enhance user experience.
Table: Human-AI Collaboration Workflow for Content Creation
| Step | AI Role | Human Role |
| 1. Research & Keyword Identification | Gather data, suggest topics, identify high-opportunity keywords, spot trends, group keywords by intent. | Choose topic, set content goals, refine keyword lists, ensure local relevance. |
| 2. Outline Generation | Generate a structured outline with headings and key points. | Review and adjust the outline, ensuring it matches search intent and covers all necessary points. |
| 3. First Draft Creation | Write the initial content based on the refined outline. | Edit, add brand voice, inject unique insights, personal experiences, and local examples. |
| 4. Refinement & QA | Suggest improvements, check for basic inconsistencies in tone (if trained). | Perform final edits, rigorous fact-checking, ensure accuracy, enhance readability, and verify brand alignment. |
| 5. SEO Optimization | Suggest keywords, meta tags, and basic on-page elements. | Ensure natural keyword use, optimize meta titles/descriptions, add internal links, and calls-to-action. |
| 6. Publication & Monitoring | (No direct role) | Publish content, monitor performance (rankings, engagement), and iterate based on data. |
Avoiding Pitfalls: Generic Content, Losing Brand Voice, and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers immense advantages, small businesses must be aware of potential pitfalls:
- Generic or Thin Content: AI can produce content that is repetitive, bland, or lacks meaningful value if not guided and edited properly. Such “low-effort” content will not perform well in search.
- Losing Your Brand Voice: Without careful training and human oversight, AI-generated text can sound inconsistent or fail to capture the unique personality of a brand.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of AI content necessitate proactive guidelines and human oversight for responsible adoption, particularly for small businesses that rely heavily on trust.
- Authenticity and Transparency: AI-generated content can lack the personal touch crucial for building trust. Transparency about AI use is vital to maintain credibility.
- Accuracy and Reliability: AI systems can learn from biased or inaccurate data, potentially spreading misinformation. Rigorous fact-checking is essential.
- Originality and Plagiarism: AI tools might inadvertently produce text that closely mirrors existing content, leading to plagiarism concerns. Ensuring content is unique and properly attributed is paramount for brand reputation.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI tools rely on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy. Protecting sensitive information is an ethical and legal imperative.
- Impact on Jobs: While AI can handle repetitive tasks, it cannot replace human creativity, strategic thinking, and empathy. This suggests a shift in job roles where AI frees up staff for higher-impact, uniquely human tasks, rather than outright displacement.
The ethical challenges of AI, including bias, potential plagiarism, and a lack of transparency, are directly mitigated by strong human oversight and clear policies. These measures are crucial for maintaining trust and preserving brand reputation, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. Responsible AI integration fundamentally requires human ethical guardianship to prevent unintended harm and ensure content remains authentic and trustworthy.
Leveraging AI for Keyword Research and Search Intent
Before writing, understanding what your audience is searching for is paramount. AI can significantly streamline keyword research, helping small businesses identify high-opportunity terms and match content to search intent.

- Identifying High-Intent Keywords: AI-powered keyword research tools can quickly identify the exact phrases customers are typing into Google, based on niche and location. This is invaluable for small businesses that don’t have the budget for expensive SEO consultants or extensive manual research.
- Understanding Search Intent: Search intent refers to the underlying purpose behind a user’s query (informational, navigational, transactional, commercial investigation). AI tools can help classify keywords by intent, allowing businesses to tailor content to directly address user needs. For local businesses, prioritizing transactional and navigational searches (e.g., “emergency plumber Brooklyn”) is often most effective, as these users are ready to take action.
- Content Clustering: AI can group related keywords into content clusters, aiding in a strategic blog strategy and ensuring comprehensive coverage of topics.
- Long-Tail Keywords: AI can suggest long-tail phrases that precisely match user intent, helping small businesses capture highly targeted traffic.
Table: Understanding Search Intent: Tailoring Content for Your Audience
| Search Intent Type | User Goal | Content Focus & Examples | AI’s Role in Identification & Creation |
| Informational | Seeking knowledge, answers, or “how-to” guides. | Comprehensive guides, tutorials, FAQs, explanations. Example: “How to fix a leaky faucet” | AI identifies questions, provides structured information, suggests related queries. |
| Navigational | Finding a specific website or page. | Direct links, contact pages, login portals. Example: “Home Depot San Diego” | AI helps ensure direct access and minimizes distractions on target pages. |
| Commercial Investigation | Researching products/services before purchase. | Comparison posts, reviews, buying guides, pros/cons. Example: “Best laptops under $1000” | AI assists in gathering product data, structuring comparisons, and suggesting features to highlight. |
| Transactional | Ready to make a purchase or take action. | Product pages, pricing pages, sign-up forms, strong CTAs. Example: “Buy AirPods Pro” | AI helps optimize value propositions, craft compelling CTAs, and address common objections. |
Maximizing Impact: SEO Best Practices for AI-Assisted Content
Beyond simply generating content, small businesses must integrate fundamental SEO best practices to ensure their AI-assisted content ranks high and drives traffic. This involves a strategic approach to keywords, content structure, user experience, and visual integration.
Keyword Strategy: Targeting High-Intent Searches
Effective keyword strategy is the cornerstone of SEO. For small businesses, it means identifying and targeting keywords that align with user intent and have a reasonable chance of ranking. The primary keyword “can Google detect AI content” and secondary keyword “free AI writer” are examples of high-intent phrases that this report itself aims to address.
AI tools make keyword research significantly easier, faster, and more effective for small businesses, enabling them to discover the precise phrases their customers are using without requiring an SEO degree or a costly consultant. These tools can identify high-opportunity keywords based on niche and location, spot trending searches, detect keyword gaps against competitors, and group keywords into content clusters for a cohesive blog strategy. This democratization of keyword research allows small businesses to compete effectively by precisely meeting user intent with targeted content.
When integrating keywords, a natural density of at least 1.5% is recommended for the primary and secondary keywords. This ensures Google understands the content’s relevance without resorting to keyword stuffing, which can harm rankings.
Content Structure and User Experience (UX): Engaging Your Audience
Once keywords are identified, the content must be structured for maximum engagement and readability. Google’s algorithms heavily weigh user engagement metrics, content depth, bounce rate, and authority as ranking factors.
- Engaging Headlines and Scannable Content: Content should be structured with clear headings (H1, H2, and H3), bullet points, and short paragraphs to make it easy to digest and understand. This improves user experience, which directly signals quality to Google.
- Strategic Internal Linking: Internal links guide users to related content within the website, improving navigation and establishing a clear site hierarchy. This encourages users to explore more pages, increasing pages per session and dwell time, both positive signals for SEO. Linking new content from established, high-authority pages also helps accelerate indexing and distribute “link equity”.
- Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Relevant CTAs encourage users to take specific actions, such as “Learn More,” “Subscribe Now,” or “Get Started”. Placing CTAs strategically, perhaps higher on the page where user attention is concentrated, can significantly improve conversion rates and guide users through the content funnel.
Optimizing content structure, internal linking, and calls-to-action directly enhances user experience, which in turn signals quality to Google and improves rankings. Google’s algorithms monitor how users interact with content, including bounce rate, dwell time, and pages per session. When users find a site easy to navigate, relevant to their needs, and engaging, they are more likely to stay longer and explore further, sending strong positive signals to Google that the content is helpful and valuable.
Integrating Images, Tables, and Infographics Effectively
Visual elements play a crucial role in enhancing content engagement and readability.
- Images and Videos: Using engaging, relevant, and optimized images and videos can significantly increase user engagement and encourage deeper interaction with the content. They can make complex information more digestible and visually appealing.
- Tables and Infographics: As demonstrated in this report, tables and infographics are excellent for presenting complex data or comparisons in a clear, scannable format. They break up text, improve readability, and can be highly shareable, further boosting engagement.
- Optimization: Ensure all visuals are optimized for web (compressed file sizes, descriptive file names, alt text) to prevent slowing down page load speed, which is a critical factor for user experience and bounce rate.
Measuring Success: Tracking Performance of AI-Assisted Content
Once AI-assisted content is published, monitoring its performance is crucial to understand its impact and identify areas for optimization. Google’s ranking factors are heavily influenced by user engagement metrics, providing direct feedback on content effectiveness.
Key User Engagement Metrics
Several key metrics provide insights into how users interact with content:
- Bounce Rate: This measures the percentage of users who leave a site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate can indicate that content is not relevant or engaging, though context is important (e.g., a single-page resource might naturally have a high bounce rate if it fully answers the query).
- Dwell Time / Average Session Duration: This indicates the amount of time users spend on a page or site. Longer dwell times suggest that content is valuable and fulfilling the user’s query.
- Pages per Session: This metric shows how many pages a user views during a single visit. A higher number indicates greater engagement and exploration of the site.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): This is the percentage of users who click on a search result after seeing it. A high CTR indicates that the title and meta description are compelling and accurately represent the content.
Google’s increased focus on user engagement metrics, particularly “engaged sessions” in Google Analytics 4 (GA4), reflects a broader shift towards evaluating content based on actual user interaction rather than just on-page SEO signals. An “engaged session” is defined as a session lasting longer than 10 seconds, having a key event, or including two or more page views. This indicates that Google is moving beyond simple keyword matching to a more sophisticated understanding of content value based on how users behave on a page. If users quickly leave a page, it signals dissatisfaction or irrelevance, which can negatively impact SEO rankings.
Using Google Search Console and Google Analytics to Monitor Performance
Small businesses can utilize free tools like Google Search Console (GSC) and Google Analytics (GA) to track the performance of their AI-generated content.
- Google Search Console: GSC provides data on search traffic and performance, showing which queries bring users to the site, impressions, clicks, and position in search results. While GSC will show AI Mode performance data, it is important to note that this data cannot currently be broken out individually to compare AI Mode performance against standard web search. This presents a challenge for small businesses trying to specifically optimize AI-generated content, as they must rely on broader site-level metrics or indirect correlations. Despite this limitation, GSC remains invaluable for identifying top queries, popular pages, and issues like low CTR, which can inform content refinement.
- Google Analytics: GA provides detailed insights into user behavior on the website, including bounce rate, average session duration, and pages per session. It allows tracking of conversions and time spent on site, which are crucial indicators of content effectiveness. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can determine if their content is engaging users and driving desired actions. If engagement rates are low, it might indicate a need to adjust content relevance or user experience.
Table: Key User Engagement Metrics & Improvement Strategies for Small Businesses
| Metric | Definition | Why it Matters for SEO | Improvement Strategies for Small Businesses |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage of single-page sessions (user leaves after viewing one page). | High rates can signal irrelevant content or poor UX, negatively impacting rankings. | Improve page load speed; create high-quality, engaging content that addresses user intent; optimize for mobile; use clear CTAs. |
| Dwell Time / Avg. Session Duration | Time users spend on a page/site. | Longer times indicate content value and relevance, a positive signal for Google. | Answer search intent early; enhance readability (headings, bullets); use multimedia (videos, images); ensure content depth. |
| Pages per Session | Number of pages a user views in one visit. | Higher numbers show greater engagement and site exploration. | Implement strategic internal linking; create content hubs/clusters; offer related content recommendations; ensure seamless navigation. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Percentage of users who click a search result after seeing it. | High CTR indicates compelling titles/descriptions and strong relevance to query. | Craft compelling meta titles and descriptions; use numbers/action words in titles; ensure title/description accurately represent content. |
Beyond the Hype: Additional Benefits and Ethical Considerations of AI for Small Businesses
While the primary focus has been on whether Google can detect AI content created by a free AI writer and how to optimize it for search, AI offers a much broader spectrum of benefits for small businesses, alongside important ethical considerations that must be addressed.
Additional Benefits of AI for Small Businesses beyond Speed and Cost
Beyond the immediate advantages of speed and cost-efficiency in content creation, AI provides significant strategic benefits for small businesses, enabling them to “punch above their weight class” in competitive markets.
- Scalability: AI tools enable businesses to generate a high volume of content quickly, allowing for rapid scaling of content marketing efforts without proportional increases in staffing or budget. This means creating multiple blog posts per week, generating numerous product descriptions, or drafting extensive website content with unprecedented speed.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI-powered tools, such as chatbots and automated outreach systems, can provide timely, personalized customer support and recommendations around the clock. This frees up human staff to focus on more complex customer service issues, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate a wide range of repetitive administrative tasks, from data entry and appointment scheduling to payroll and invoice processing. This streamlines daily operations, reduces manual errors, and allows staff to concentrate on high-impact, growth-oriented work.
- Improved Decision-Making and Audience Analysis: AI can analyze vast amounts of historical data and consumer behavior to provide predictive analytics, forecast demand, optimize pricing, and anticipate customer needs. For marketing, AI can help create detailed audience personas, refine online advertising strategies, and facilitate A/B testing for tailored messaging. This data-driven approach leads to more effective marketing campaigns and better resource allocation.
- Internal Document Generation: AI is highly effective at generating basic internal documents, such as training materials, meeting agendas, and customer correspondence. This can significantly reduce the time spent on routine administrative tasks for lean small business teams.
- Sales Optimization: AI tools can analyze historical sales data to predict sales trends, identify and prioritize leads, track customer sentiment, and recommend next steps for sales representatives, helping small teams close deals faster.
The expansive benefits of AI extend far beyond content creation for small businesses, offering strategic advantages in operations, customer relations, and market analysis. This allows them to effectively compete with larger entities by enhancing efficiency, personalizing customer interactions, and making more informed business decisions.
Addressing Ethical Challenges and Responsible AI Adoption
Despite the immense potential, the adoption of AI, particularly for content generation, comes with critical ethical considerations that small businesses must proactively address to maintain trust and reputation.
- Authenticity and Transparency: AI-generated content can sometimes lack the genuine personal touch that builds strong relationships and trust with audiences. For small businesses, where personal connection is often a cornerstone of customer loyalty, this is a significant challenge. It is essential to be transparent about the use of AI in communications, as clear disclosure helps maintain credibility and ensures the final content genuinely reflects the brand’s voice.
- Accuracy and Reliability: AI systems learn from existing data, which may contain inherent biases or inaccuracies. This means AI-generated content could inadvertently spread misinformation or reflect undesirable biases if not rigorously reviewed. Small businesses, often with limited resources for extensive fact-checking, must implement stringent procedures to ensure all messages are reliable and precise.
- Originality and Plagiarism: AI tools, trained on vast datasets, carry the risk of producing text that closely mirrors existing content, potentially leading to plagiarism issues. A unique brand voice is vital for standing out, and inadvertent plagiarism could severely damage a brand’s reputation and lead to legal complications. Therefore, verifying content originality and proper attribution is crucial.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI tools often rely on large amounts of data, raising significant concerns regarding data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive information is an ethical and legal imperative, requiring diligence in ensuring AI tools comply with data privacy regulations.
The ethical challenges inherent in AI, such as potential bias, plagiarism, and a lack of transparency, are directly mitigated by robust human oversight and the establishment of clear policies. These measures are crucial for maintaining trust and brand reputation, particularly for small businesses that depend on strong community and customer relationships. Responsible AI integration fundamentally requires human ethical guardianship to prevent harm and preserve the authenticity and trustworthiness of content.
Furthermore, while AI can efficiently handle repetitive and data-intensive tasks, it cannot replicate the nuanced creativity, strategic thinking, and empathy that human writers bring to content creation and communication. This perspective suggests a transformation in job roles rather than outright displacement. AI frees up human talent from mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities that require unique human skills, such as building customer relationships, developing innovative strategies, and crafting emotionally resonant narratives. This complementary relationship allows small businesses to maximize efficiency while preserving the indispensable human element in their operations.
Conclusion: Empowering Small Businesses in the AI Content Era
The central question, “Can Google detect AI content created by a free AI writer?” has been thoroughly explored, and the answer remains consistently clear: No, Google cannot reliably detect AI-generated content. The compelling evidence, such as the erroneous flagging of the United States Constitution as AI-written, highlights the inherent limitations and unreliability of current AI detection technologies. Google’s sophisticated algorithms do not penalize content based on its authorship, but rather on its inherent quality and helpfulness to the user.
For small businesses, this understanding is profoundly empowering. It removes the fear of algorithmic penalties based purely on AI usage and redirects focus to what truly matters: creating content that is valuable, comprehensive, and engaging for their audience. The “Helpful Content System” and the E-E-A-T framework are Google’s primary mechanisms for assessing quality, emphasizing Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. These principles are not just SEO tactics but foundational business practices that build genuine trust with both search engines and customers.
The strategic use of AI for content creation is not about replacing human effort but augmenting it. The optimal approach involves a “human-AI partnership” where a “free AI writer” generates initial drafts, and human editors then refine, fact-check, inject brand voice, add unique insights, and ensure accuracy and nuance. This human touch is indispensable for transforming generic AI output into high-quality, E-E-A-T-compliant content that resonates with readers.
Furthermore, AI extends its benefits beyond content creation, offering small businesses significant advantages in keyword research, audience analysis, customer experience, and operational efficiency, enabling them to compete more effectively. However, responsible AI adoption necessitates a proactive approach to ethical considerations, including transparency, data privacy, originality, and the impact on human roles. These challenges are best navigated through strong human oversight and clear policies, ensuring that AI enhances, rather than compromises, a business’s integrity and reputation.
In essence, small businesses should embrace AI tools not as a shortcut to bypass quality, but as a powerful lever to scale their content efforts and improve overall business operations. By prioritizing helpfulness, adhering to E-E-A-T principles, diligently applying human editing, and continuously monitoring performance through tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics, small businesses can confidently leverage AI to achieve higher search rankings, attract more customers, and foster sustainable growth in the digital age. The future of content is a collaborative one, where the synergy between human creativity and artificial intelligence unlocks unprecedented opportunities for success.
Frequently Asked Questions: Can Google Detect AI Content?
Below are the most common questions small business owners ask about using AI writers and Google’s content policies, with practical answers to help you confidently create AI-assisted content that ranks well:
Can Google detect AI content when I use a free AI writer for my business website?
No, Google cannot reliably detect AI content created by free AI writers or any other AI tools. The question “can Google detect AI content” has a definitive answer: Google’s algorithms focus on content quality and helpfulness rather than detecting whether content is AI-generated. Even when businesses wonder “can Google detect AI content” from popular tools, the reality is that Google evaluates content based on user value. As long as your content provides genuine value to users, addresses search intent, and demonstrates E-E-A-T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), Google cannot detect AI content origins and won’t penalize it.
If Google can’t detect AI content, how can I ensure my AI-generated content ranks well?
Since the answer to “can Google detect AI content” is no, focus on content quality instead of hiding AI usage. Follow the “AI to draft, human to polish” approach:
- Add personal experiences and unique insights
- Inject your brand’s voice and personality
- Fact-check all claims and statistics
- Ensure content directly answers user questions
- Structure content with clear headings and scannable formatting
- Include relevant internal links and calls-to-action
Remember, while Google can’t detect AI content, it can identify low-quality content regardless of its source.
Do I need to worry about AI detection tools if Google can’t detect AI content?
No, you shouldn’t worry about third-party AI detection tools when asking “can Google detect AI content.” These external tools are notoriously unreliable—they even flagged the US Constitution as AI-generated! Since Google can’t detect AI content and doesn’t use these flawed tools for ranking decisions, focus on content quality instead. Google’s stance clarifies that the question “can Google detect AI content” is less relevant than whether your content helps users. Transparency about AI usage can build trust, but the priority should be content quality over detection concerns.
What makes AI content rank well if Google can’t detect AI content anyway?
When people ask “can Google detect AI content,” they’re often missing the bigger picture. Google can’t detect AI content, but it can identify helpful versus unhelpful content regardless of origin. High-ranking AI content typically:
- Provides unique value and actionable insights
- Demonstrates real expertise and experience
- Is well-researched and factually accurate
- Directly answers user questions
- Feels authentic to your brand voice
Low-ranking content (AI or human) usually:
- Feels generic or mass-produced
- Lacks original insights or personal experience
- Contains factual errors or outdated information
- Doesn’t address user search intent clearly
Can Google detect AI content in sensitive industries like healthcare or finance?
The question “can Google detect AI content” remains the same across all industries—Google cannot reliably detect AI content regardless of the topic. However, for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics, content quality standards are much higher. While Google can’t detect AI content in these sectors, it does scrutinize content quality more carefully. If you operate in sensitive industries:
- Always have qualified professionals review and approve content
- Cite authoritative medical, financial, or legal sources
- Include proper disclaimers about professional advice
- Consider having licensed professionals author or co-author content
- Prioritize accuracy over content production speed
Even though Google can’t detect AI content, the stakes for accuracy are higher in these fields.

